Key Terms:
Watersheds
Hydrology
Surface Water
Ground Water
A watershed is also known as a drainage basin and is the geographic area where surface water runs off to a low point or outlet of the basin.
The Eastern Sierra is at the western edge of the Great Basin, which is a region that includes parts of Nevada, Utah, Idaho, Oregon, and California. The Great Basin is named as such because it is a region that does not drain to the ocean at all. Rather, the Great Basin is made of many different watersheds that are all terminal (also known as closed or endorheic) basins, where water flows to a low point within the basin and there is no outlet.
In the Eastern Sierra, the Owens Basin and the Mono Basin are hydrologically separate watersheds that LADWP artificially connected with the construction of the Mono Craters Tunnel in 1941. Both are terminal basins, with Mono Lake and Owens Lake being the low points where water naturally flows to in each watershed. Because the Mono and Owens Basins are now connected through LADWP’s infrastructure, they are sometimes referred to as a single watershed known as the Mono-Owens Basin.
hydrology basics
Hydrology
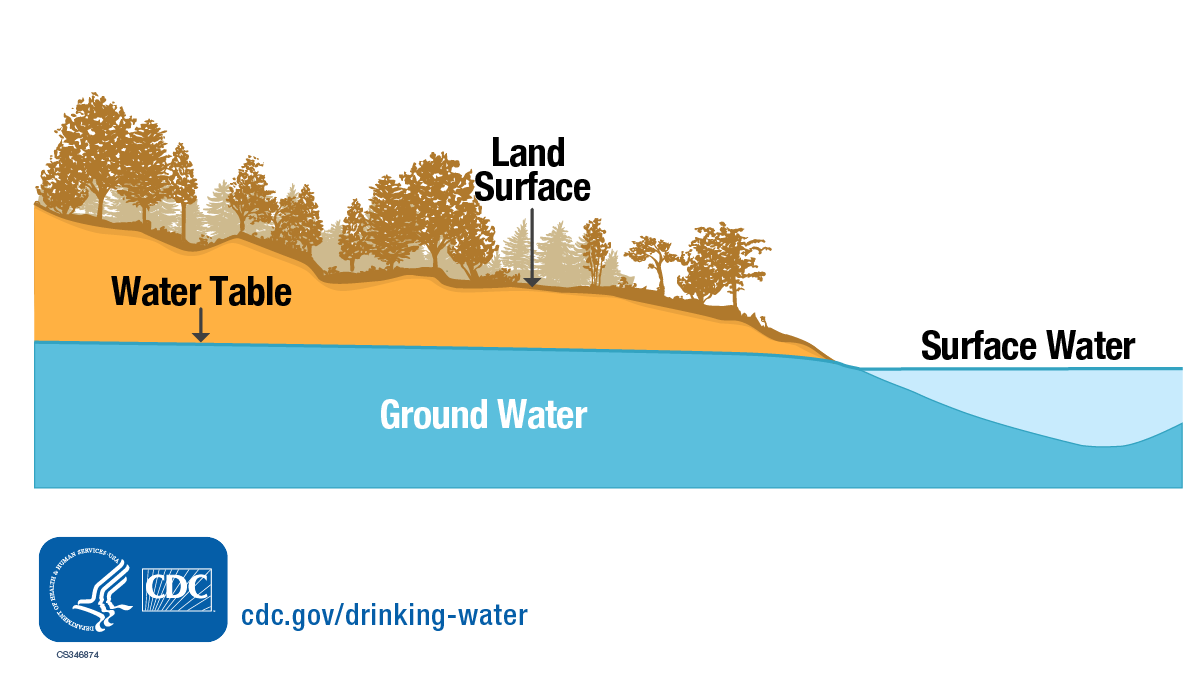
The water that you see in creeks, ponds, or lakes is surface water. There is also water that you cannot see, which is underneath the ground in aquifers and is known as groundwater. Surface water and groundwater are connected although it is not always obvious. In some places, surface water sinks into the earth and recharges groundwater. Groundwater may also discharge to the surface in springs or artesian wells or by providing base flow to rivers.
Surface Water
The surface water of the Mono and Owens Basins mostly originates from snowpack at high elevations. Rainfall is limited in the Eastern Sierra, and in the Owens Valley only averages 5.4 inches per year. Melted snowpack flows in streams and creeks, known as tributaries, into larger bodies of water like rivers and lakes. Springs also contribute to surface flow.
Ground Water
The water that is under the surface of the earth is called groundwater. An aquifer is the layer of underground rock or sediment in which that groundwater is held. About 30% of the earth’s freshwater is stored in aquifers.
The valley floor of the Owens Basin is naturally characterized by a high (or shallow) water table, which supports sources of surface water such as springs, and affects the vegetation that is able to grow and the overall environment. Groundwater is pumped for various uses via production wells, which can affect the groundwater available for the environment.
How are springs and seeps affected by groundwater?
How are rivers affected by groundwater?